Radix Sort
Faster sorting algorithm
Consider all the sorting algorithms below;
- Insertion Sort
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Heap Sort
They are all based on comparison model. Comparison sorts only use comparison to determine relevant order of elements.
The best worst-case running time of all the comparison sorts is O(nlgn).
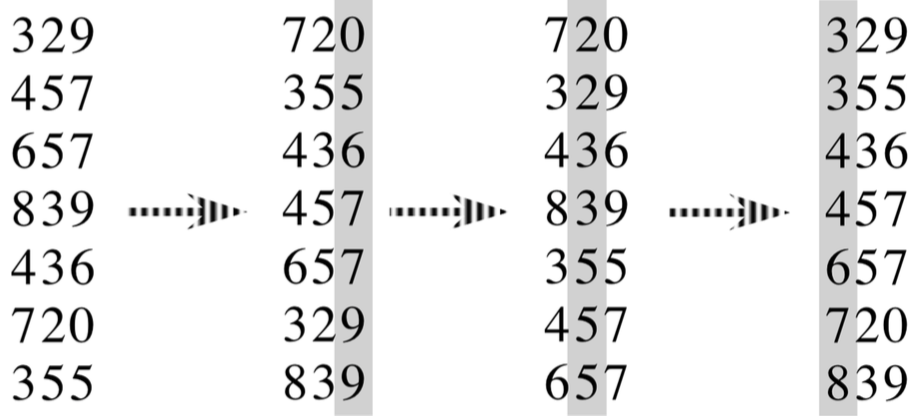
Radix sort
- Sort on least significant digit or most significant digit
- Sort again on second-least significant digit
- Repeat for all digits
Radix Sort Pseudo code
RADIX-SORT(A,d)
for i=1 to d
COUNTING-SORT(A[i]) //this counting sort takes O(n)
Radix Sort time analysis
| Best case | Worst case | average case |
|---|---|---|
| O(dn) | O(dn) | O(dn) |
The execution of radix sort algorithm sorts repeatedly from least-significant digit to most-significant digit; therefore, how many passes we need to sort would affect the performance. The number of passes is dependent on how many buckets we choose to have and how may digits we would like to sort in one pass. For instance, 16-bit unsigned integer can represent numbers in the range of 0 to 65536. If we decided to use 4 digits in one pass, the number of buckets would become , and we will end up having passes. Thus, the time complexity of radix sort is to sort n numbers with passes, and is the maximum number of distinct values in one pass. b represents the total number of bits and r is the number of bits to be examined in one pass. Choosing r = lgn and b = dlgn would results in the time complexity becoming where d is digits to be sorted and n is the number of elements in the input array. Therefore, the value of d would affect the performance while keeping r and b the same.

Least significant digit vs Most significant digit
Least significant digit radix sort: logical concatenation of the sorted bins after each pass. Most significant digit radix sort: recursive sorting each bin independently after each pass. (e.g., sorting bytes 256 bins after first pass, 65536 bins after second pass, 16777216 (16 million) bins after third pass and so on)
Sorting algorithm comparison
| Algorithm | Data Structure | Best case | Average case | Worst case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insertion sort | Array | O(n) | O(n^2) | O(n^2) |
| Quicksort | Array | O(nlgn) | O(nlgn) | O(n^2) |
| Mergesort | Array | O(nlgn) | O(nlgn) | O(nlgn) |
| Heapsort | Array | O(nlgn) | O(nlgn) | O(nlgn) |
| Radixsort | Array | O(dn) | O(dn) | O(dn) |
