Heap Sort
Heap Data Structure
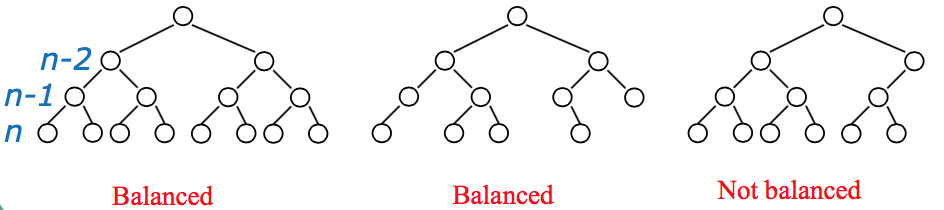
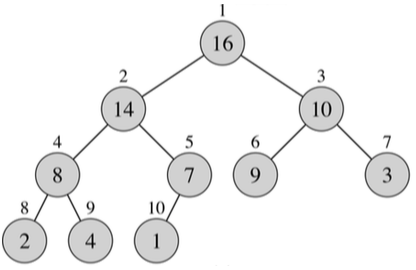
A binary heap data structure is an array object that we can view as a nearly complete binary tree with the following properties:
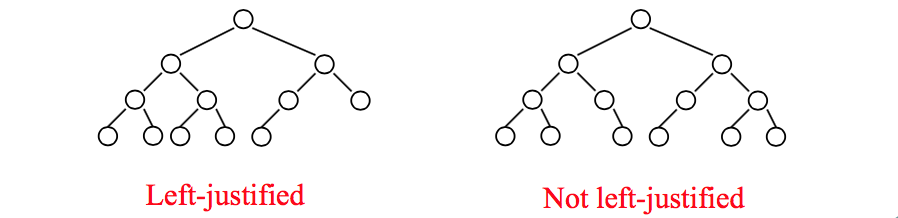
- Structural property: all levels are full, except possibly the last one. The last one can be filled from left to right (left justified)
- Order property: For any node x, Parant(x) >= x
Heap Sort
- Build a max-heap from the array
- Swap the root (max. element) with the last element in the array.
- “Discard” this last node by decreasing the heap size
- New root may violate max heap property, but its children are max heaps.
- MAX-HEAPIFY to fix this.
- Repeat this process until only one node remains
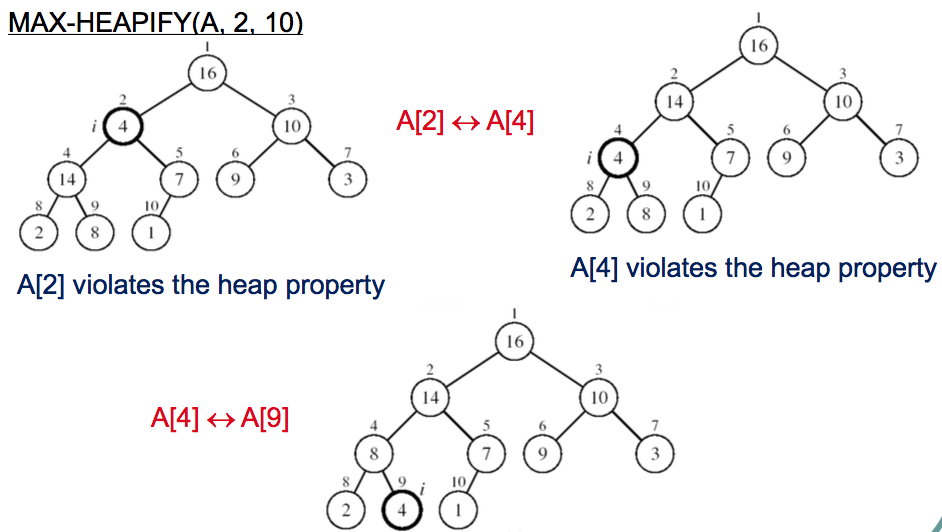
MAX-HEAPIFY
What is MAX-HEAPIFY? Try to restore Max Heap property
Heap Sort example
Input array = [7, 4, 3, 2, 1]
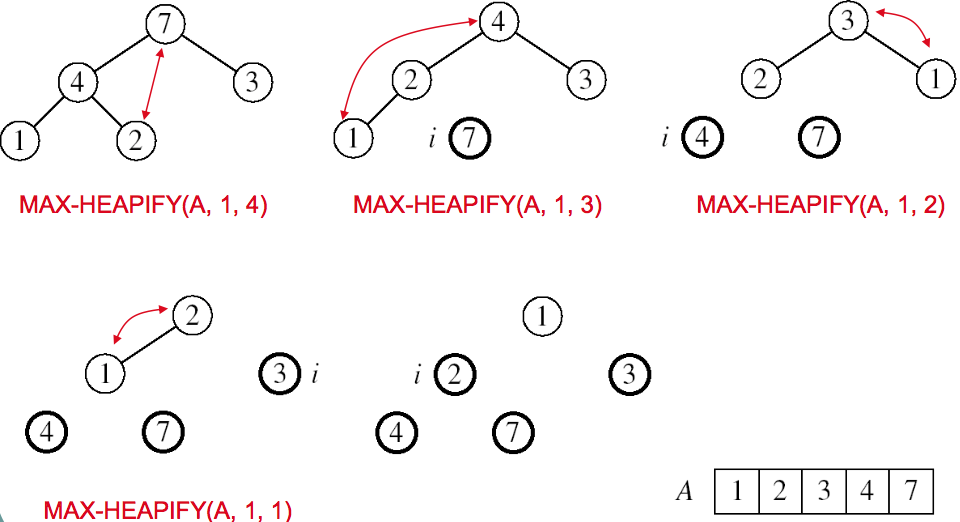
Heap Sort Pseudo code
RADIX-SORT(A,d)
for i=1 to d
COUNTING-SORT(A[i]) //this counting sort takes O(n)
Heap Sort time analysis
| Best case | Worst case | average case |
|---|---|---|
| O(nlgn) | O(nlgn) | O(nlgn) |
This algorithm sorts an array using heap representations. After building MAX-HEAP tree, it extracts the max element by swapping the root element with the last one, which is O(n). Then, the algorithm will call MAX-HEAPIFY to fix the heap which is O(lgn). Therefore, the time complexity for all cases would be O(nlgn) for any inputs. In other words, the processing time for this case will grow as the rate of as n increase. For building MAX-HEAP as the initial step of Heap sort, the number of computations can be varied depending on how input is ordered. For instance, the input array sorted in decreasing order would take less swapping than the one sorted in increasing order. However, after building a MAX-HEAP which will take a linear time, the max element is to be extracted and MAX-HEAPIFY will be executed which takes O(lg n) time. Thus, the running time would still be O(nlgn).